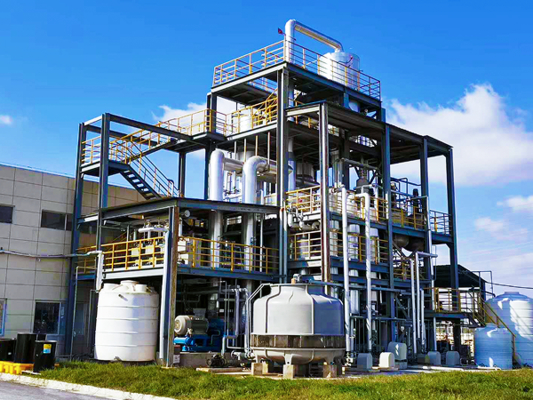
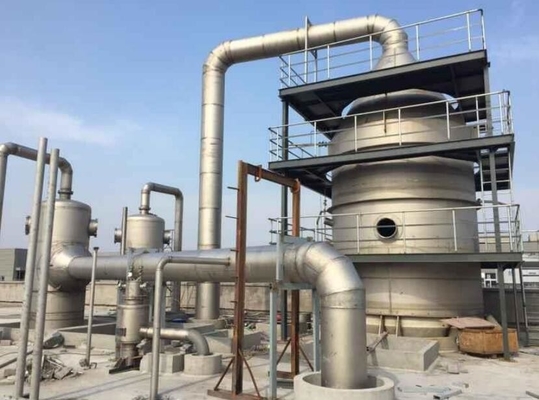
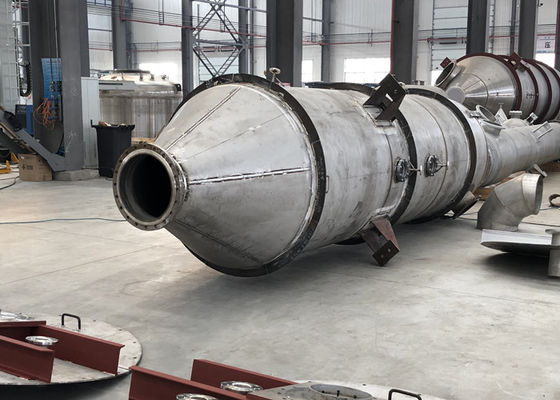
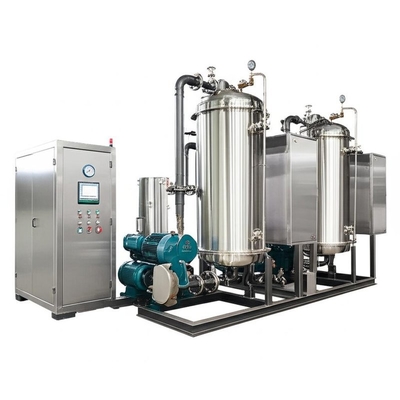
Efficient MVR Evaporator For Chemical/Environmental Protection With Customized Pressure

Engineer-to-order
MVR (Mechanical Vapor Recompression) evaporator optimized for
chemical processing and
environmental protection/ZLD. The system features
customized pressure setpoints (vacuum levels and compression ratios) to match product thermal limits, fouling tendencies, and regulatory discharge targets--delivering
high energy efficiency, stable quality, and predictable OPEX.
Key Benefits
- Energy Savings: Recycles latent heat via mechanical recompression; minimal fresh steam after start-up.
- Pressure Tailoring: Application-specific vacuum and compressor discharge pressure for optimum ΔT and throughput.
- Quality & Compliance: Low boiling temperatures protect product; high-quality condensate supports reuse and discharge limits.
- High Availability: 24/7 continuous duty with redundancy, CIP-ready design, and predictive fouling monitoring.
- Broad Compatibility: Handles high-salinity brines, RO/NF concentrates, dye/printing effluents, pharma/chemical liquors.
Process & Pressure Control
Secondary vapor is mechanically compressed to raise saturation temperature and reused as the heating medium. Pressure setpoints (evaporator shell vacuum and compressor discharge) define the operating Δ T/LMTD, enabling low-temperature evaporation for heat-sensitive feeds or higher-rate modes for robust duties.
Controls & Safety
Closed-loop regulation of level, pressure, ΔT, and conductivity; interlocks for compressor/VFD, vacuum/NCG handling, condensate quality guard, and overload protection. Power-quality mitigation (AFE/filters) available per site codes.
Materials & Cleanability
Wetted parts in SS316L/duplex (Ti/Hastelloy on request), drainable layouts, anti-scale dosing, and validated CIP for long campaigns. Surface finishes and elastomers selectable for chemical/environmental duties.
Process Overview -- Customized-Pressure MVR
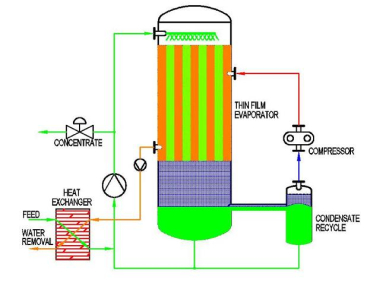
- Feed conditioning: filtration/softening, pH trim, and deaeration to minimize scaling/corrosion.
- MVR evaporation (vacuum): compressor speed sets discharge pressure; shell pressure/vacuum defines boiling point.
- Condensate management: polishing (if required) to meet reuse/discharge limits (COD/TOC/cond).
- Concentrate routing: to crystallizer/centrifuge/dryer for solids discharge or upstream recycle per flowsheet.
- Automation: recipes for different feeds with pressure/ΔT profiles; alarm interlocks and remote diagnostics.
Key Components
- MVR evaporator/forced-circulation body with circulation pumps and vapor-liquid separator
- Mechanical vapor compressor (turbo/Roots) with VFD for pressure/ΔT control
- Main heater, preheaters, condensers, vacuum/NCG handling skid
- PLC/HMI/SCADA with historian; instrumentation (T/P/flow/cond/level)
- CIP skid; anti-scale dosing; optional condensate polishing filters/RO
Performance & Sizing
| Parameter |
Typical Range* |
| Operation |
Continuous, 24/7 |
| Shell pressure (vacuum) |
~6-25 kPa(abs) typical (duty-dependent) |
| Compressor discharge pressure |
~45-120 kPa(abs) typical (sets ΔT and capacity) |
| Electric use (MVR) |
~15-40 kWh per ton of water evaporated |
| Fresh steam demand |
Very low after start-up (backup/ancillary only) |
| Turndown |
50-100% with stable ΔT and quality |
| Availability |
≥95-98% with redundancy and planned CIP |
| Materials |
SS316L / duplex; Ti/Hastelloy on request |
*Actual performance depends on feed characteristics, viscosity/fouling tendency, compression ratio, and heat-transfer design.
FAQ
Can you match our required vacuum/pressure window?
Yes. We engineer compressor CR, VFD range, and exchanger area to hit the target shell vacuum and discharge pressure.
How do you balance energy use and capacity?
By tuning discharge pressure/ΔT and circulation rate; recipes allow low-temperature quality mode or high-throughput mode.
Is it suitable for ZLD and high-salinity brines?
Absolutely--options include anti-scale dosing, forced-circulation crystallizer, and solid handling for ZLD compliance.
Application


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 
















