Modular Multiple-Effect Falling Film Evaporator with Vacuum Crystallization for Wastewater (Paper & Salt Industries)
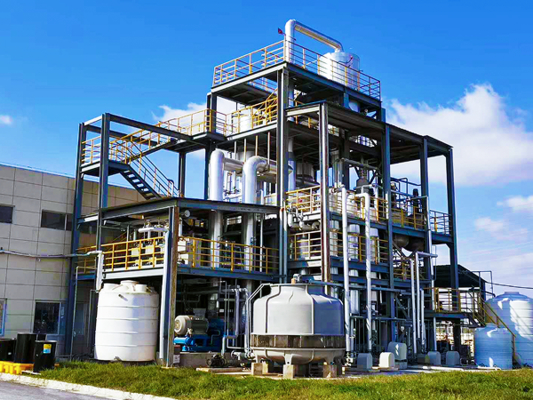
A removable, skidded MEE line engineered for polluted water concentration and salt recovery. The system applies falling/thin-film evaporation across multiple effects under vacuum, followed by vacuum crystallization, delivering low steam consumption, compact footprint, and stable, continuous operation.
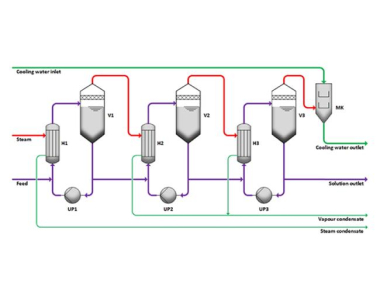
Process Description — Example Parallel-Flow Principle
The feed enters the first-effect evaporator circuit, mixes with the circulating liquor, and is heated with live steam in heater H. In evaporator V1, water vaporizes while the solution reaches its boiling temperature. The partially concentrated liquor then flows to the second effect, which operates at lower temperature and pressure. Vapors from the first effect act as the heating medium for the second effect. This staged reuse of vapor continues across effects, depending on boiling point elevation and operating constraints, maximizing thermal efficiency and minimizing utility demand.
Structure
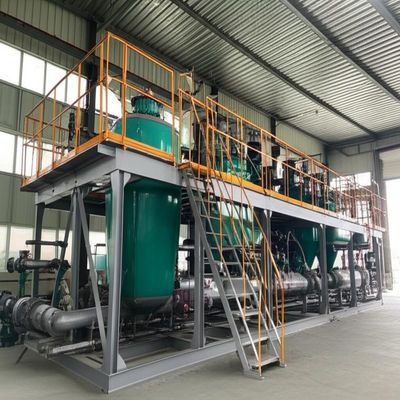
A typical multiple-effect falling film line comprises first/second/third-effect heaters and separators, pre-heaters, terminal condenser, vacuum system, feed/circulation/discharge/condensate pumps, interconnecting piping & valves, and instrumentation (vacuum gauge, thermometers, pressure gauges, flowmeters, level, and conductivity where required). Skid-mounted sections enable removal and maintenance without lengthy shutdowns.
Key Characteristics
- Evaporation rate: 500 kg/h to 80 t/h (standardized range).
- Materials: Stainless steel SS304 or SS316L.
- Closed, vacuum operation: Rapid evaporation at low temperatures with short residence time.
- Sanitary internals: Mirror-polished seamless tubes reduce fouling and ease CIP.
- Low evaporation temperature: Optional re-induction of secondary steam (e.g., spray hot-pressure pump) improves heat use and reduces product thermal exposure.
- High concentration ratio: Falling film hydrodynamics handle higher viscosities, resist scaling, and enable short concentration times.
- Automation: PLC/HMI with interlocks and data logging; recipe-based operation.
- Process flexibility: Configurable trains to match feed chemistry, BPE, and client utilities; TVR/MVR can be integrated if required.
Steam Economy
Each additional effect reuses the previous effect’s vapor as a heat source—drastically cutting fresh steam per kg of evaporation.
Vacuum Crystallization
Stable crystal formation and cleaner condensate for reuse or compliant discharge.
Modular & Maintainable
Removable modules and accessible piping reduce downtime and simplify overhauls.
Applications
Designed for paper-making effluent, salt-making brines, and a broad range of industrial wastewaters in chemical, pharmaceutical, textile/dyeing, breweries, food & beverage, and ZLD pretreatment. Desalination RO reject concentration and resource recovery are also supported.
Typical Three-Effect Falling Film Evaporator — Specifications & Technical Parameters
| Parameter / Specifications |
HP-3.0 |
HP-4.5 |
HP-6.0 |
HP-9.0 |
HP-12.0 |
HP-15 |
HP-20 |
HP-24 |
HP-30 |
HP-50 |
| Evaporation capacity (kg/hr) |
3000 |
4500 |
6000 |
9000 |
12000 |
15000 |
20000 |
24000 |
30000 |
50000 |
| Consumption of raw steam (kg/hr) |
900 |
1350 |
1800 |
2700 |
3600 |
4500 |
4500 |
7200 |
9000 |
15000 |
| Vacuum degree of each effect |
First Effect |
0 |
|
Second Effect |
448 |
| (mmHg) |
Third Effect |
640 |
| Evaporation temperature of each effect |
First Effect |
99 |
|
Second Effect |
76 |
|
Third Effect |
53 |
| Steam pressure for evaporation (MPa) |
0.6–1.0 (Absolute pressure) |
| Solid content in feed (%) |
6–7 (example) |
| Solid content outlet (%) |
42–48 (example) |
Operation Notes
- Effect count and duty sized to meet target steam economy and condensate quality.
- Vacuum levels and ΔT set per feed BPE and scaling tendency.
- Optional TVR/MVR modules can be integrated to further reuse secondary vapors.
Our Production Site

 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!